When the fact table contains huge number of rows, then the query to calculate at higher dimension levels will take longer time, because of the need to scan full dataset; another reason is with how ROLAP works, without aggreation (pre-calculation), ROLAP will read detail data from database tables and calculate on the fly.
To solve the performance issue with huge fact tables, we can build aggregate tables which contain pre-calculated summary data. The build of aggregate tables should be a part of the ETL process that populate / refresh the data warehouse.
We will use "Aggregation Designer" to help design the aggregate tables.
1) Start "Pentaho Aggregation Designer"; (can be downloaded from http://mondrian.pentaho.com)
2) Config the "Database Properties"; In this sample, we use Oracle database.
3) Connect to Data Source, using the OLAP schema file that we created before, as shown below:

4) then click "Connect" button. Once the schema has been consumed and parsed, the Aggregation Designer performs a series of validations to ensure the database is suitable for creation and the validation result is displayed.
5) we can use "Aggregation Designer" in two ways - Manual or Automated (Advisor). For demo purpose, I manually created two Aggregations.

6) to export the aggregation design, click "Export" button.
From the "Export and Publish" window, we can Preview the scripts for creating the aggregation tables; Create the aggregation tables; or Populate the aggregation tables; or Export (save) the Mondrian Schema file (with definition for aggregations) for deploy on Mondrian OLAP server.

4. Deploy Schema File in Mondrian
Suppose that Mondrian OLAP server is setup. (for how to install & config Mondrian OLAP server, please see my other article.)
1) Put the schema file "SalesHistory.xml" under: TOMCAT_HOME/webapps/mondrian/WEB-INF/queries;
2) Create file "datasources.xml" under: TOMCAT_HOME/webapps/mondrian/WEB-INF. This file may look like this:
<DataSources>
<DataSource>
<DataSourceName>Provider=Mondrian;DataSource=MondrianFoodMart;</DataSourceName>
<DataSourceDescription>Mondrian FoodMart Data Warehouse</DataSourceDescription>
<URL>http://localhost:8080/mondrian/xmla</URL>
<DataSourceInfo>Provider=mondrian;Jdbc=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl1;
JdbcUser=sh;JdbcPassword=xxx;JdbcDrivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver;
Catalog=/WEB-INF/queries/SalesHistory.xml
</DataSourceInfo>
<ProviderName>Mondrian</ProviderName>
<ProviderType>MDP</ProviderType>
<AuthenticationMode>Unauthenticated</AuthenticationMode>
<Catalogs>
<Catalog name="SalesHistory">
<DataSourceInfo>Provider=mondrian;Jdbc=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl1;
JdbcUser=sh;JdbcPassword=xxx;JdbcDrivers=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver;
Catalog=/WEB-INF/queries/SalesHistory.xml
</DataSourceInfo>
<Definition>/WEB-INF/queries/SalesHistory.xml</Definition>
</Catalog>
</Catalogs>
</DataSource>
</DataSources>
3) modify the file "mondrian.properties" under: TOMCAT_HOME/webapps/mondrian/WEB-INF/classes
Add the following two lines to allow the use of aggregates:
mondrian.rolap.aggregates.Use=true
mondrian.rolap.aggregates.Read=true
4) re-start the Tomcat server;
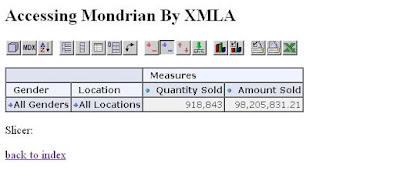
5) to test that the deployed OLAP schema is working, modify the file "xmla.jsp" under: TOMCAT_HOME/webapps/mondrian/WEB-INF/queries;
Replace the MDX query with the following one:
SELECT {[Measures].[Quantity Sold], [Measures].[Amount Sold]} ON columns,
Hierarchize({([Gender].[All Genders], [Location].[All Locations])}) ON rows FROM [Sales]
WHERE ([Time].[All Times])
Save the change, and click the following:
http://localhost:8080/mondrian/testpage.jsp?query=xmla
(to be continued)
No comments:
Post a Comment